C1: Targets for antiviral strategies against ZIKV
Dr. Daniela Bender
Paul-Ehrlich-Institut
Bundesinstitut für Impfstoffe
und biomedizinische Arzneimittel
Paul-Ehrlich-Straße 51-59
63225 Langen
Tel.: +49 (0)6103-77 5411
E-Mail: Daniela.Bender(at)pei(dot)de
Prof. Dr. Eberhard Hildt
Bundesinstitut für Impfstoffe
und biomedizinische Arzneimittel
Paul-Ehrlich-Institut
Paul-Ehrlich-Straße 51-59
63225 Langen
Tel.: +49 (0)6103-77 2140
Fax: +49 (0)6103-77 1234
E-Mail: Eberhard.Hildt(at)pei(dot)de
Project description:
Zika viruses (ZIKV) are arboviruses, which belong to the flaviviridae family. During the ZIKV outbreak in Brazil in 2016, where a considerable number of microcephaly cases in newborns was associated with ZIKV infection during pregnancy. The WHO declared a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC). At present neither a preventive vaccine or antiviral drugs are available. By inhibition of virus replication in an early phase of the viral life cycle if applicable as a temporary preventive approach, the viral load could be significantly reduced. Thereby, the spread of the virus would be impaired and the risk of an intrauterine infection would be reduced. During the first funding period target structures could be identified.
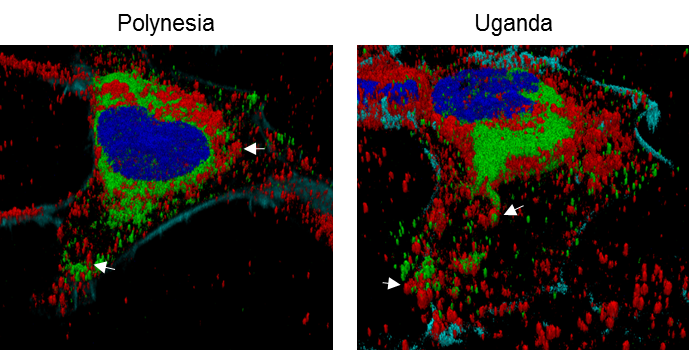
Intracellular distribution of tetherin (red) and ZIKV envelope protein (green) in cells that were infected either by the Uganda or the French Polynesia isolate.
Scientific goal:
Based on already identified targets and further targets, antiviral strategies are developed, the underlying mechanisms will be investigated and the effect on additional members of the flaviviridae family will be studied.
DRUID Collaboration partners:
A2 Grünweller lab, B1 Diderich/Kolb lab, B6P Herker lab, C2 Kempf lab, C5 Glebe/Geyer lab, D1 Steinmetzer lab, E6 Schiffmann/Laux lab
References C1: 1. Herrlein et al. (2021) J Virol. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02117-2 2. Sabino et al (2021)., J Virol. doi: 10.1128 3. Maddaluno et al., 2020 EMBO Mol Med. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201911793 4. Basic et al. 2019 Antiviral Res. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.104644. 5. Akhras et al. (2019) Viruses doi: 10.3390/v11080748. 6. Sabino et al., (2019) doi: 10.3390/v11060524 7. Elgner et al (2018) Viruses doi: 10.3390/v10040149


