E1: Platform Drug Testing Against Helminths
PD Dr. Simone Häberlein
Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen
BFS, Institut für Parasitologie
Schubertstraße 81
35392 Gießen
Tel.: +49 (0)641-99 38476
Fax: +49 (0)641-99 38469
E-Mail: Simone.Haeberlein(at)vetmed.uni-giessen(dot)de
Prof. Dr. Christoph Grevelding
BFS, Institut für Parasitologie
Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen
Schubertstraße 81
35392 Gießen
Tel.: +49 (0)641-99 38466
Fax: +49 (0)641-99 38469
E-Mail: Christoph.Grevelding(at)vetmed.uni-giessen(dot)de
Project description:
Targets of antiparasitic compounds are often conserved, which opens the possibility to achieve therapy of different parasitic infections with the same active compound. In platform project E1, we focus on parasitic worms (helminths), for which the discovery of new active compounds is particularly important because of resistances or suboptimal therapeutic successes of existing drugs. To this end, we implement in vitro screenings of compounds originating from DRUID projects to test their efficacy against the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni (causing schistosomiasis) and the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica (causing fascioliasis). The platform project cooperates with several national and international partners, including colleagues in endemic countries in Asia and Africa, who open us test possibilities against numerous other helminths species.
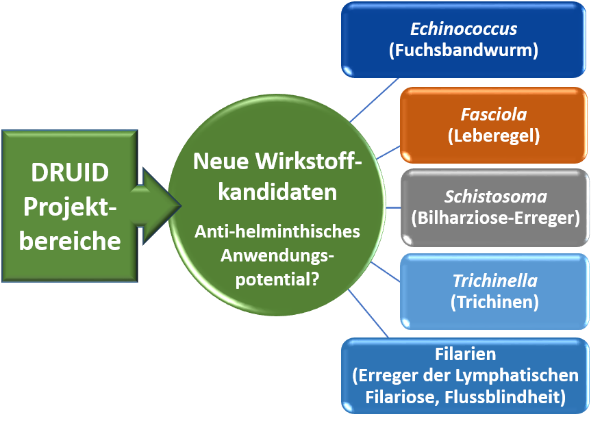
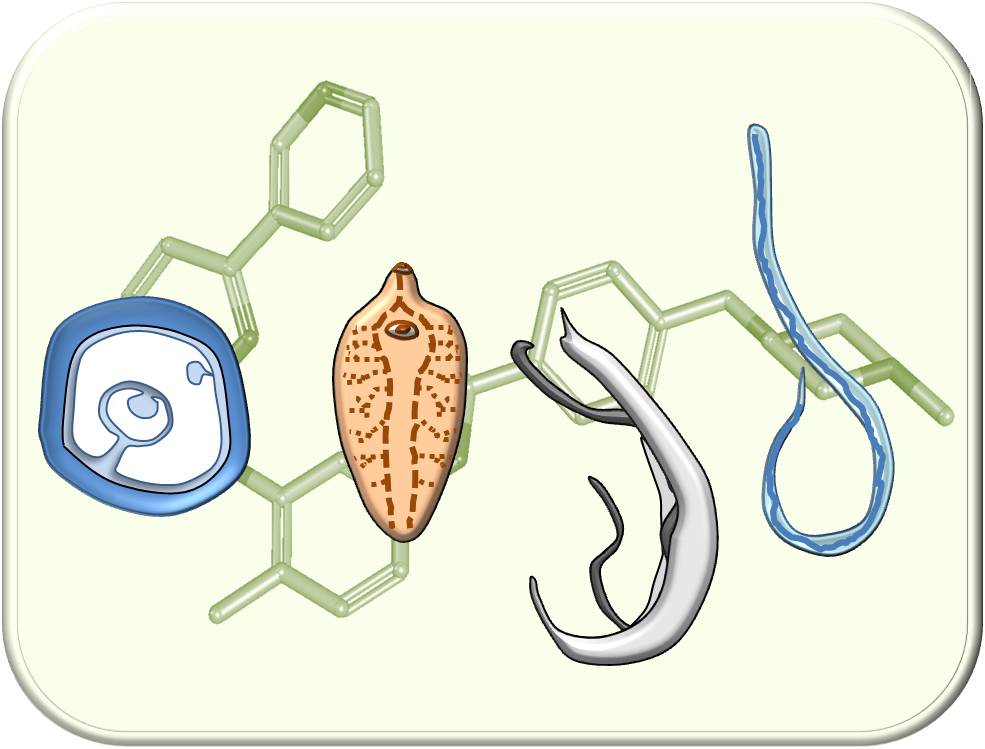
Strategy for identifying active compounds with broad antiparasitic efficacy against globally important helminths species. ©Simone Häberlein
We also investigate the mechanism of action for selected test compounds by applying various in vitro culture-based and imaging methods.
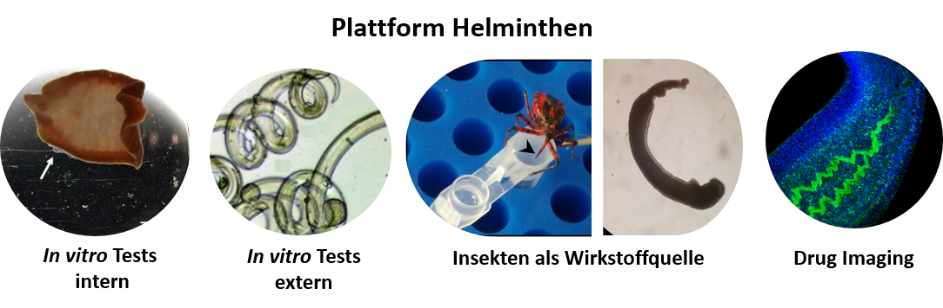
Test spectrum provided by the platform project to identify and characterize anthelminthic compounds. ©Simone Häberlein, Miray Tonk-Rügen
Scientific goal:
Aim of the project is the identification of substances with a broad anti-parasitic efficacy and the discovery of conserved modes of action.
DRUID Collaboration partners:
A2 Grünweller lab, A6 Douglas lab, A7 Przyborski lab, B4 Schlitzer lab, B5 Grevelding lab, B7 Falcone lab, E4 Spengler lab
References E1: 1. Peter-Ventura et al. (2019) ChemMedChem 14(21):1856-1862. 2. Houhou et al. (2019) Sci Rep 9:15867. 3. Li et al. (2019) Parasitol Res 118(3):881-890. 4. Morawietz et al. (2020) Front Vet Sci 7:611270. 5. Kellershohn et al. (2019) PLOS Negl Trop Dis 13:e0007240. 6. Tonk et al. (2020) Antibiotics 9:664. 7. Mokosch et al. Anal Bioanal Chem 413(10): 2755-2766. 8. Mughal et al. (2021a) Int J Parasitol 51(7):571-585. 9. Mughal et al. (2021b) Int J Parasitol S0020-7519(21)00312-X. 10. Gallinger et al. (2022) Pharmaceuticals 15(2): 119. 11. Morawietz et al. (2022) Parasitol Res (online ahead of print) doi: 10.1007/s00436-021-07388-1


